Why Violations are Costly for Banks
The term compliance refers to adherence to laws, regulations, and internal policies and procedures. A single violation may result in civil penalties, costly audits, and even criminal penalties if fraud or intentional misconduct is proven. Beyond direct financial penalties, organizations face significant risks such as reputational damage, resource drain, and stricter enforcement by supervisory authorities.
In banking and insurance, trust is the core of every customer relationship. That means companies must not only comply with complex requirements such as GDPR, Dodd-Frank, HIPAA, PCI DSS, or DORA, but also build systems to detect potential violations, conduct risk assessments, and implement corrective measures. By tailoring safeguards and maintaining thorough documentation, institutions can better uphold compliance requirements, mitigate risks, and strengthen long-term stability.
Penalties in the Financial Sector at Record Levels
Growing financial market regulation is reflected in record fines and enforcement actions by supervisory authorities such as the SEC, ESMA, and BaFin. Among the most common regulatory infractions are breaches of documentation and reporting duties. The complete recording of communication and business data remains one of the sector’s greatest challenges. Off-channel communication, incomplete archives, or missing disclosures often trigger costly penalties per violation.
- In January 2025, twelve financial companies agreed to pay a total of more than $63 million to settle SEC investigations into compliance violations of business communication retention requirements.
- In February 2024, sixteen other companies had already accepted civil penalties totaling more than $81 million, also for widespread failures to comply with U.S. rules and regulations regarding record-keeping obligations.
- The strictness of the authority is also evident in an international comparison: according to an analysis by European Business Magazine, in 2024, around 90 percent of all global bank fines exceeding $500,000 were imposed on institutions in the US, corresponding to a total volume of $4.5 billion.
The Most Common Civil Violations

The most common causes for warnings include incomplete records, off-channel communication, lack of transparency in customer information, and data protection breaches. Typical issues are a missing legal basis, insufficient consent, violations of privacy and security rules, or weak technical and organizational measures.
These areas highlight that consistent recording, clear information obligations, and solid data management are crucial to avoid regulatory infractions and mitigate risks effectively. Regular risk assessments and employee training help organizations strengthen confidentiality, uphold civil rights, and comply with frameworks.
These examples make it clear that when organizations violate obligations, the costs can run into the millions. The impact goes beyond visible financial sanctions and often requires corrective, legal, and operational measures.
An Overview: The Most Important Regulatory Requirements
Compliance officers must take into account numerous compliance laws, regulations, and internal guidelines. The following overview presents a summary of the most important global and regional regulations that financial institutions must observe and comply with.
| Regulation | Scope | Possible sanctions | Typical violations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDPR | EU / Data protection for personal data | Up to €20 million or 4% of annual turnover | The supervisory authorities impose heavy fines if companies process personal data without a legal basis. A single compliance violation can cost millions. |
| MiFID II (2025) | EU / Financial markets Fines in the millions, license revocation | Fines in the millions, license revocation | Banks and securities firms are required to record all customer conversations. Regulatory authorities consider violations to be a serious compliance risk that can be punished with license revocation or fines in the millions. |
| FCA | UK / Financial supervision | Financial supervision Fines, public warnings | The UK financial supervisory authority emphasizes transparency and customer protection. Violations of these compliance requirements can result in heavy penalties and public warnings. |
| Dodd-Frank Act | USA / Financial market regulation | Heavy fines, criminal proceedings | In the U.S., regulatory authorities strictly check whether transactions are fully recorded and archived. Compliance violations often lead to criminal proceedings. |
| HIPAA | USA / Health data (relevant for insurers) | Up to US$1.5 million per category per year | All covered entities are required to enforcing the hipaa privacy rule. For insurers and health data processors, any disclosure of sensitive patient data is considered a serious breach of compliance requirements and is subject to heavy penalties by the regulatory authorities for HIPAA violations. |
| PCI DSS | International / Credit card data | US$5,000–100,000 per month until remediation | Companies that store or transmit credit card data in an unsecure manner are committing serious compliance violations. Fines are often imposed on a monthly basis until the requirements are fully met. |
Why Non Compliance is More Expensive Than Expected
Financial penalties are often only the first visible damage. In practice, regulatory infractions cause far-reaching burdens that significantly strain budgets, resources, and reputations.
These indirect costs can exceed visible sanctions many times over. To avoid such outcomes, companies must raise awareness at all levels, build systems to identify and remedy violations, and ensure that every employee understands their role in adhering to rules and regulations.
Efficient and structured risk management is essential: ethical standards, regular employee training, and effective monitoring are crucial. In the long term, this approach helps organizations comply with obligations, mitigate risks, and safeguard their future viability.
Compliance as a Competitive Advantage: Trust Makes the Difference
Compliance is no longer just a regulatory requirement, but a central element of brand and reputation management.
Financial service providers that demonstrably ensure compliance with laws and measure themselves against the highest standards create trust, security, and transparency for all stakeholders: regulatory authorities, business partners, and, above all, customers.
This means:
The more complex the legal requirements become, the more compliance culture and governance develop into real competitive advantages. Companies that invest in preventive measures, intelligent automation and monitoring, and ongoing training minimize compliance risks and gain lasting trust in a sensitive market environment.
Compliance Challenges
Omnichannel
Financial institutions today are faced with the task of recording all customer communications – whether traditional telephone contact in the service center, interactions via collaboration platforms, mobile apps, or emails. A consistent omnichannel strategy with reliable and legally compliant archiving offers a decisive advantage: it brings together different data sources in a consistent manner, ensures complete documentation, and actively supports institutions in reliably meeting regulatory requirements.
Cloud
The use of cloud technologies offers enormous advantages in terms of scalability and flexibility. At the same time, however, the requirements for data protection, data residency, and auditability are increasing. Especially in highly regulated industries, a secure cloud infrastructure is therefore crucial for reliably complying with legal requirements and avoiding compliance violations from the outset.
Artificial intelligence
The ever-growing volume of communications is overwhelming manual review processes. AI creates the basis for making compliance more efficient within the company: anomalies can be detected automatically, risk assessments can be carried out proactively, and potential violations can be identified at an early stage. The key challenge lies in using AI systems in such a way that they not only work efficiently, but also ensure the necessary transparency and traceability for audits.
Minimizing Risks: How AI Provides Effective Support
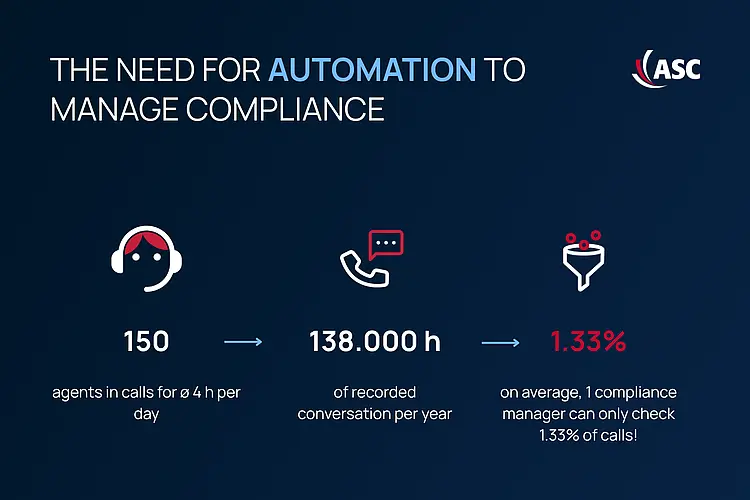
Manual review of communication data is no longer practical today.
AN Example:
Manual review of communication data is no longer practical today. In a company with 150 employees who spend four hours a day in customer conversations, this amounts to around 138,000 hours of recorded conversations per year. A single compliance manager can only manually review a tiny fraction of this, leaving the majority of communications unmonitored.
ASC as a Partner for Compliance in Customer Communications
ASC supports regulated customers with specialized compliance software and native solutions to reliably, securely, and legally record communication data and archive it in a legally compliant manner. The AI Policy Engine can identify potential risks in conversations and possible violations at an early stage. Preconfigured and industry-specific compliance templates for (2025) II, Dodd-Frank, and FCA automatically check whether communications are compliant and flag anomalies in real time to help ensure compliance with laws and regulations. Each detection is documented in an audit-proof manner, which greatly facilitates control and traceability for internal and external compliance audits.
Thanks to seamless integration with Microsoft Cloud for Financial Services and Microsoft Teams, the company benefits from a scalable, secure cloud architecture – ideal for hybrid working models and highly regulated industries.
As a certified provider of compliance recording in Microsoft Teams, ASC ensures that financial institutions can record, analyze, and store customer conversations in a legally compliant, traceable, and secure manner in the Microsoft Cloud for Financial Services.
In regulated industries such as finance, trust is the most valuable asset, and compliance plays a key role in maintaining it. Once lost, it is difficult to regain. Together with ASC, we help organizations securely record customer communications and evaluate them in the Microsoft Cloud in a compliant manner using AI.
Advantages at a Glance:
- Preconfigured templates for MiFID II, FCA, and Dodd-Frank.
- Automated AI tools for monitoring and reporting for risk assessment and transparent documentation.
- Seamless integration with Microsoft Teams and certified for Microsoft Cloud for Financial Services.
- Support for industry-specific requirements.
An effective compliance management system is essential today to minimize risks, avoid heavy fines, and strengthen stakeholder confidence. Compliance not only encompasses adherence to legal regulations, but also shapes corporate culture. A consistent compliance culture promotes integrity, strengthens public trust, and supports sustainable corporate governance.
With innovative technologies and a strong partner like ASC, compliance is not seen as a burden, but as a competitive advantage. With the right technologies and partners, financial institutions can not only avoid heavy penalties, but also strengthen the trust of their customers and partners in the long term. ASC offers a scalable and secure solution that not only ensures compliance, but also actively facilitates it by supporting the implementation of guidelines.